Table of Contents
- 2.1. The entry parentFile
- 2.2. User dependent configuration
- 2.3. Command-Line Options
- 2.4. General Configuration Options
- 2.5. Billing System Configuration Options
- 2.6. Network Configuration Options
- 2.7. Network Address Translation Configuration Options
- 2.8. Load Balancing Configuration Options
- 2.9. BaseApp Configuration Options
- 2.10. BaseAppMgr Configuration Options
- 2.11. Bots Configuration Options
- 2.12. CellApp Configuration Options
- 2.13. CellAppMgr Configuration Options
- 2.14. DBMgr Configuration Options
- 2.15. LoginApp Configuration Options
- 2.16. Reviver Configuration Options
The single most important configuration file on the server is
<res>/server/bw.xml,
where <res> is the
resource tree used by the server (usually specified in
~/.bwmachined.conf).
All sever processes read this file. It contains many parameters, all of which are described in this chapter. The default values are appropriate for many different games, and care should be taken when changing them, since it might affect performance.
On the description of the parameters, please note the following:
-
Boolean parameters should be specified as true or false.
-
Where a tag is specified as
tag1/tag2, the second tag is specified inside the scope of the first one. For example, the tag dbMgr/allowEmptyDigest is specified as:
<dbMgr> <allowEmptyDigest> true </allowEmptyDigest> </dbMgr>
The entry parentFile in the configuration file specifies the next file in the chain of files where BigWorld should look for an entry for a configuration option.
To assign a default value to a configuration option, BigWorld follows the steps below:
-
Searches for an entry for the configuration option in file
<res>/server/bw.xml. -
If the file does not contain an entry for the configuration option, then the chain of configuration files is inspected, until the entry is found.
-
If the entry is not specified in any of these files, a hard-coded default is used.
All default values for a production environment are stored in file
bigworld/res/server/production_defaults.xml. The file
bigworld/res/server/development_defaults.xml
specialises this with default values for a development environment.
Typically, the entry parentFile in file
<res>/server/bw.xml is
set to either server/production_defaults.xml or
server/development_defaults.xml, and only non-default
options are stored in your server/bw.xml.
The example below shows the configuration option maxCPUOffload in section balance having its default value overridden:
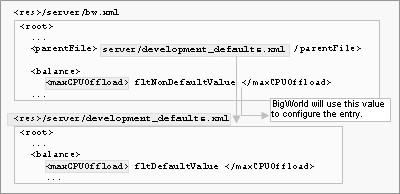
Overriding default values for configuration options
A file that is user dependent can be used instead of
bw.xml. This is useful to allow multiple users to run from
the same resource tree. In a production environment, for example, you may
run the resources using a test user before using the production
user.
If a file with the name server/bw_<username>.xml
exists, this is used as the start of the server configuration chain
instead of server/bw.xml.
Typically, the parentFile section in this file would
refer to server/bw.xml and only options specific to the user,
such as dbMgr/databaseName would be in this file.
The configuration options specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
can also be overridden via command-line arguments.
To override a default value, add arguments in the format +optionName value.
The example shows the baseApp section's configuration option pythonPort having its default value changed to 40001, and the option archivePeriod changed to 0:
baseapp +baseApp/pythonPort 40001 +baseApp/archivePeriod 0
Values changed via the command line are not sent to components started via BWMachined. This includes using WebConsole, control_cluster.py, and components started by a Reviver process.
The list below describes the general configuration options:
-
bitsPerSecondToClient (Integer)
Desired default bandwidth from server to the client. To calculate the number of bytes to be sent in each packet, the formula below is used (where UDP_OVERHEAD is 28 bytes):
packetSize = (bitsPerSecondToClient / 8 / gameUpdateHertz) - UDP_OVERHEAD
-
channelTimeoutPeriod (Float)
Number of seconds before an anonymous channel will timeout. An example of these are channels from the BaseApps and CellApps to the DBMgr. If a process becomes unresponsive for this amount of time, the DBMgr will drop the channel to this process.
This setting should be significantly larger than baseAppMgr/baseAppTimeout and cellAppMgr/cellAppTimeout.
-
debugConfigOptions (Integer)
Level of logging information generated when processing configuration parameters in file
<res>/server/ bw.xml.The possible values are described in the list below:
-
0
No log is generated.
-
1
A log message is generated for each configuration option read.
-
2
A verbose message is generated for each configuration option read.
-
-
desiredBaseApps (Integer)
Number of BaseApps that need to be running for the server to start.
-
desiredCellApps (Integer)
Number of CellApps that need to be running for the server to start.
-
desiredServiceApps (Integer)
Number of ServiceApps that need to be running for the server to start.
-
externalInterface (String)
Network adapter interface to use for external communication, if not explicitly set by the server component.
In a production environment, BaseApps are recommended to have two Ethernet adapters: one adapter connected to the Internet, and a separate one connected to the internal LAN.
During development, there is no problem with using the same interface.
Accepted formats are:
-
Adapter name — Examples: eth0, eth1
-
IP[/netmask] — Examples: 10.5.2.1, 10.0.0.0/8, 192.168.5.0/24
-
Domain name — Examples: intern0.cluster/24, extern5.cluster/24
This value can be overridden by a tag with same name in the following sections:
-
baseApp — For more details, see BaseApp Configuration Options.
-
loginApp — For more details, see LoginApp Configuration Options.
-
-
externalLatencyMax (Float)
Maximum number of seconds by which packets sent from the server process will be artificially delayed. Each packet will be randomly delayed between this value and externalLatencyMin.
This value can be overridden by a tag with the same name in the following sections:
-
baseApp — For more details, see BaseApp Configuration Options.
-
loginApp — For more details, see LoginApp Configuration Options.
This feature is useful for testing during development.
See also externalLossRatio, xref_externalLatencyMin
-
-
externalLatencyMin (Float)
Minimum number of seconds by which packets sent from the server process will be artificially delayed. Each packet will be randomly delayed between this value and externalLatencyMax.
This value can be overridden by a tag with the same name in the following sections:
-
baseApp — For more details, see BaseApp Configuration Options.
-
loginApp — For more details, see LoginApp Configuration Options.
This feature is useful for testing during development.
See also xref_externalLossRatio, xref_externalLatencyMax
-
-
externalLossRatio (Float)
Proportion of outgoing packets that will be dropped by this processes external nub to simulate loss on the external network. This is a value between 0.0 and 1.0 indicating what proportion of packets will be dropped.
This value can be overridden by a tag with the same name in the following sections:
-
baseApp — For more details, see BaseApp Configuration Options.
-
loginApp — For more details, see LoginApp Configuration Options.
This feature is useful for testing during development.
See also xref_externalLatencyMin, xref_externalLatencyMax
-
-
gameUpdateHertz (Integer)
Number of times per second that the server should send an update to the clients. This corresponds to the game tick frequency.
-
hasDevelopmentAssertions (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether server should be aggressive in its use of assertions.
This option should be set to true during development, and to false when running a production server.
For example, if this option is set to true, then a corrupted packet sent from a client can cause an assertion on the server, while if this is set to false, then only an error message is generated and the server component continues to run.
-
internalInterface (String)
This tag is deprecated, and its use is not recommended. For details, see the document Server Overview's section Server Components → BWMachined → BWMachined Interface Discovery.
Network adapter interface to use for internal communication, if not explicitly set by the server component.
Accepted formats are:
-
Adapter name — Examples: eth0, eth1
-
IP[/netmask] — Examples: 10.5.2.1, 10.0.0.0/8, 192.168.5.0/24
-
Domain name — Examples: intern0.clust/24, extern5.clust/24
This value can be overridden by a tag with the same name in the following sections:
-
baseApp — For details, see BaseApp Configuration Options.
-
baseAppMgr — For details, see BaseAppMgr Configuration Options.
-
cellApp — For details, see CellApp Configuration Options.
-
cellAppMgr — For details, see CellAppMgr Configuration Options.
-
dbMgr — For details, see DBMgr Configuration Options.
-
loginApp — For details, see LoginApp Configuration Options.
-
-
internalLatencyMax (Float)
Maximum number of seconds by which packets sent from the application's internal nub will be delayed.
For more details, see internalLatencyMin.
See also internalLossRatio.
-
internalLatencyMin (Float)
Minimum number of seconds by which packets sent from the application's internal nub will be delayed.
Each packet will be randomly delayed between this value and internalLatencyMax.
This feature is useful for testing during development.
This value can be overridden by a tag with the same name in the following sections:
-
baseApp — For details, see BaseApp Configuration Options.
-
baseAppMgr — For details, see BaseAppMgr Configuration Options.
-
cellApp — For details, see CellApp Configuration Options.
-
cellAppMgr — For details, see CellApp Configuration Options.
-
dbMgr — For details, see DBMgr Configuration Options.
-
loginApp — For details, see LoginApp Configuration Options.
-
reviver — For details, see Reviver Configuration Options.
See also options internalLatencyMax and internalLossRatio.
-
-
internalLossRatio (Float)
Proportion of packets on this application's internal nub that will be dropped to simulate loss on the internal network. This is a ratio between 0.0 and 1.0.
This feature is useful for testing during development.
This value can be overridden by a tag with the same name in the following sections:
-
baseApp — For details, see BaseApp Configuration Options.
-
baseAppMgr — For details, see BaseAppMgr Configuration Options.
-
cellApp — For details, see CellApp Configuration Options.
-
cellAppMgr — For details, see CellApp Configuration Options.
-
dbMgr — For details, see DBMgr Configuration Options.
-
loginApp — For details, see LoginApp Configuration Options.
-
reviver — For details, see Reviver Configuration Options.
See also options internalLatencyMax and internalLatencyMin.
-
-
loggerID (String)
The ID used by the process when registering with MessageLoggers. If this ID does not match a MessageLogger's filter, the process will not log to that MessageLogger. (For details on MessageLogger, see Message Logger).
Multiple BigWorld servers can share the same logger process. If this behaviour is not desired, then you can use a unique loggerID per server instance — this will cause MessageLogger to filter out all messages that do not match the loggerID it has been told to monitor.
-
logSpamPatterns (List of Strings)
A list of log message prefixes can be specified which will be suppressed on a per-second basis if the number sent to MessageLogger exceeds a certain threshold. Note that this is not intended a mechanism to sweep error messages "under the carpet"; it is designed to reduce the network load that can be generated by log traffic, which tests have indicated can be in excess of actual game traffic in some situations if suppression is disabled.
This option can be overridden by a tag with the same name in any app section. Note that the overriding does not merge the suppression lists, it simply replaces the global list with the one defined at the app level.
Additionally, the list of suppression patterns can be modified at runtime using the
logger/addSpamSuppressionPatternandlogger/delSpamSuppressionPatternwatchers.Please see
bigworld/res/server/production_defaults.xmlfor an example of a suppression list. -
logSpamThreshold (Integer)
The number of a particular log message that can be sent to MessageLogger in a single second before suppression will take place. Note that only messages matching one of the
<logSpamPatterns>(see above) will be suppressed. -
maxOpenFileDescriptors (Integer)
Set a minimum value for the number of simultaneous open file descriptors an application can have open. The default maximum for this value is 16384 for applications started from bwmachined, and 1024 for applications started directly, but that maximum can be adjusted using the 'ulimit -n' shell built-in command or by changing the pam_limits configuration.
This is particularly useful for increasing the maximum number of simultaneous bots that a single bots process can create.
The default value of -1 causes the app to not attempt to change this value on startup.
-
monitoringInterface (String)
Network adapter interface to use for non-game communications, such as logging output, telnet sessions, and watcher requests. For example: eth0.
See the BaseApp's configuration option externalInterface for accepted formats.
-
networkCompression/external (String)
The type of compress to use on large some external messages sent over the network. The supported options are NONE and ZIP. For zip compression, a compression level can be set between 1 and 9 with 1 being the fastest and 9 being the best compression.
<networkCompression> <internal> ZIP <level> 3 </level> </internal> <external> NONE </external> </networkCompression>
This setting can be overwritten entity type via NetworkCompression/external section of the entity type's
.deffile. -
networkCompression/internal (String)
The type of compress to use on some large internal messages sent over the network.
This setting can be overwritten entity type via NetworkCompression/internal section of the entity type's
.deffile.See networkCompression/external for more information.
-
numStartupRetries (Integer)
Number of times that CellApps and BaseApps will try to locate other components when starting up.
Each attempt is one second apart, so this value roughly indicates the number of seconds that these two components can be started before the other 'global' server components have started.
-
outputFilterThreshold (Integer)
Value used to filter the messages that are printed and sent to the logger.
All messages are tagged with an integer value. If the message number is greater than or equal to the filter value, then the message is allowed (the bigger the value, the more messages are filtered out).
For example, a threshold of 2 allows only INFO messages and higher (TRACE and DEBUG messages are filtered out).
The possible values and their message thresholds are described in the list below:
-
0 — MESSAGE_PRIORITY_TRACE
-
1 — MESSAGE_PRIORITY_DEBUG
-
2 — MESSAGE_PRIORITY_INFO
-
3 — MESSAGE_PRIORITY_NOTICE
-
4 — MESSAGE_PRIORITY_WARNING
-
5 — MESSAGE_PRIORITY_ERROR
-
6 — MESSAGE_PRIORITY_CRITICAL
-
7 — MESSAGE_PRIORITY_HACK
-
8 — MESSAGE_PRIORITY_SCRIPT
-
-
personality (String)
Name of the personality module for the server.
This module should contain things such as methods to be called back from the server (for example, when the server is ready). The personality module is usually named after your game.
If not specified, the module named
BWPersonalityis used. -
production (Boolean)
If set to true, enables the server processes to run in a production mode which makes a best attempt at emitting ERROR messages when encountering configuration settings that are considered detrimental for a production environment. In rare cases this may also prevent server processes from starting if the configuration options are seen to be completely unrealistic for a production environment.
Currently this is a global configuration option and cannot be set per server application type.
-
shutDownServerOnBadState (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether server should be shut down when in an unrecoverable state.
Currently, the following scenarios are handled:
-
All CellApps are dead.
-
An attempt to restore Base entities after a BaseApp crash fails. This could happen if:
-
All BaseApps are dead.
-
Two BaseApps die in quick succession. This can cause the loss of base entities that were on the first BaseApp to crash and being backed up on the second BaseApp to crash.
-
-
-
shutDownServerOnBaseAppDeath (Boolean)
If set to true, the entire server will be shut down if a single BaseApp dies. Normally, the fault tolerance system would allow the server to continue running.
-
shutDownServerOnCellAppDeath (Boolean)
If set to true, the entire server will be shut down if a single CellApp dies. Normally, the fault tolerance system would allow the server to continue running.
-
shouldUseChecksums (Boolean)
If set to true, then all packets sent between server components will be checksummed to verify their correctness. This is in addition to the UDP checksum automatically provided by the Linux kernel and protects against packet corruption by buggy network drivers. If a corrupted packet is detected by Mercury (meaning that it has somehow passed the UDP checksum), you will see an error message like:
ERROR Packet::validateChecksum: Packet (flags 178, size 1459) failed checksum (wanted 3dc56738, got 9fe7000a)
If after running servers for long enough and not seeing this error message you feel confident that the UDP checksum is reliable enough on your hardware, you can disable this option for a small performance improvement. The checksum is very simple and fast to calculate so this is likely to have only a small impact on performance.
-
shuttingDownDelay (Float)
Number of seconds that the server should wait before a requested controlled shutdown is actually performed.
-
tickStatsPeriod (Float)
Number of seconds between ticking statistics that keep a moving average. There can be a lot of statistics that need to be ticked. If too much time is spent maintaining these statistics, consider increasing this value. The time taken ticking statistics is measured by the tickStats profile. For example, see
profiles/summaries/tickStatswatcher value. -
timeSyncPeriod (Float)
Number of seconds between each synchronisation of game time between CellAppMgr and other applications.
-
useDefaultSpace (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether to automatically create an initial space when he server starts.
This option is ignored if spaces are loaded from the database during start-up.
The configuration options specified in this section relate to user authentication and billing systems.
-
billingSystem/authenticateViaBaseEntity (Boolean)
This option is used to indicate that user authentication and billing system integration will be done via base entity script.
If true, the usual user authentication done by DBMgr is bypassed and a base entity of type entityTypeForUnknownUsers is always created. The DBMgr attempts to load the entity with the username. If this does not exist, a new entity is created.
This new entity is not initially stored in the database. It is up to the base entity script to call
Base.writeToDB()if it wants the entity to persist.See also option entityTypeForUnknownUsers.
-
billingSystem/entityTypeForUnknownUsers (String)
This specifies the type of the entity to create when shouldAcceptUnknownUsers or authenticateViaBaseEntity are used.
See also options shouldAcceptUnknownUsers and shouldRememberUnknownUsers.
-
isPasswordHashed (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether the password stored in the database's bigworldLogOnMapping table is hashed. Hashing is recommended for security reasons. With hashing, it is very difficult to determine the original password from the database. For more details, see Default Authentication via MySQL.
-
billingSystem/shouldAcceptUnknownUsers (Boolean)
If true, a user can log in with an unknown login name and a new entity of type specified in entityTypeForUnknownUsers will be created.
See also options entityTypeForUnknownUsers and shouldRememberUnknownUsers.
-
billingSystem/shouldRememberUnknownUsers (Boolean)
If true, the entity created for an unknown user will be stored in the database and an account record will be stored for this entity. This option is only used when shouldAcceptUnknownUsers is true.
See also option shouldAcceptUnknownUsers.
-
billingSystem/type (String)
Setting as to which billing system to use. Not all values are valid depending on the type of BigWorld package you have purchased. Possible valid values are:
-
bwauth
This billing system is only intended for use by the Indie version of BigWorld which authorises client login accounts against an online service. It is compiled into the DBMgr and is not able to be modified.
-
custom
This billing system is an example of a custom billing system implemented in C++ as available in the files
bigworld/src/server/dbmgr/custom_billing_system.. In order to compile this billing system into DBMgr you need to toggle the Makefile variable USE_CUSTOM_BILLING_SYSTEM in[ch]ppbigworld/src/server/dbmgr/Makefile. -
standard
This is the standard billing system used by BigWorld in which account information is stored in DBMgr's MySQL database and Python hooks are available to customise the login / authorisation process.
-
The configuration options specified in this section relate to network communication and the behaviour of various aspects of communication channels.
The options specified in the following list are specifically related to the behaviour of channels when packets start overflowing. This can occur when the send window fills up and buffering of packets is required in order to handle packet resends.
The maximum packet options defines a per channel type threshold to assist in preventing channels from using indefinite amounts of memory while buffering overflow packets.
-
maxChannelOverflow/isAssert (Boolean)
Specifies whether the offending channel should raise a program assertion, effectively terminating the process, when the maximum number of overflow packets has been reached. This only applies to internal channels and does not apply for channels to client applications.
-
maxChannelOverflow/external (Integer)
Number of packets to allow to overflow on an external channel before raising an ERROR message, or ASSERT'ing if <isAssert> has been set to true. A value of 0 disables any log messages and assertions from occurring.
-
maxChannelOverflow/internal (Integer)
Number of packets to allow to overflow on an internal channel before raising an ERROR message, or ASSERT'ing if <isAssert> has been set to true. A value of 0 disables any log messages and assertions from occurring.
-
maxChannelOverflow/indexed (Integer)
Number of packets to allow to overflow on an indexed channel before raising an ERROR message, or ASSERT'ing if <isAssert> has been set to true. A value of 0 disables any log messages and assertions from occurring.
An indexed channel is a channel that is used for communicating directly between the cell and base parts of an entity.
The configuration options specified in this section relate to running the server behind a NAT (Network Address Translator). This may be useful during development to allow a BigWorld server to run behind a NAT'ing firewall.
These configuration options are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under the section <networkAddressTranslation>,
and are described below:
-
externalAddress (String)
Address to be returned to client if he is outside the server cluster LAN.
If the client is outside the server cluster LAN (the option localNetMask is used to determine that), then LoginApp will return the IP address set in this option, instead of the address that the BaseApp thinks it is on.
This option is intended for use only during development, when the machines that the BaseApps are running on do not have real IP addresses (i.e., they are behind a NAT'ing firewall), but you still want clients to log in from the Internet.
See also option localNetMask.
-
localNetMask (String)
Mask to be used against the client's IP address in order to determine whether he is inside the server cluster LAN.
The net mask is an IP address followed by the number of bits to match. For example, 10.0.0.0/8 would match any IP starting with 10 (i.e., 10.*.*.*). The default is 0.0.0.0/0, in which case no redirecting will be done.
If it is determined that the client is not on the server cluster LAN, the LoginApp will return the IP address set in option externalAddress.
See also option externalAddress.
The load balancing configuration options are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under the section <balance>, and are described
below:
-
aggressionDecrease (Float)
When load balancing, if the movement of a partition changes direction, the aggression of that partition's movement is decreased by this amount. This helps avoid thrashing if the load balancing continuously overshoots its mark.
A larger value will make thrashing less likely but will reduce the responsiveness in these occasions.
This value should be in the range 0.1 to 1.0.
-
aggressionIncreasePeriod (Float)
This is the minimum number of seconds taken to revive back to the same level of aggression after an aggressionDecrease has been applied.
This is used to calculate how much the aggression should revive each balance tick if movement continues in the same direction.
-
maxAggression (Float)
This is the maximum aggression that can be reached. Typically this would be about 1.
During load balancing, the CellAppMgr attempts to offload work between Cells. With an aggession of 1, it will try to move the its optimal position immediately. If aggression is less than this, it will attempt to offload only this fraction of the optimal load amount.
-
maxAggressionIncreasePeriod (Float)
This is the minimum number of seconds taken to revive from the minimum aggression level to the maximum aggression level.
A smaller value for this increases the rate of recovery from a period of minimum aggression to maximum aggression.
-
maxCPUOffload (Float)
Maximum estimated amount of CPU processing that can be offloaded from a cell to another in one tick of load balancing.
A larger value should result in faster changes to the server's load balancing. This value is a fraction of 100% CPU usage, and its range is from 0.0 through 1.0, but is likely to always be less than 0.1.
-
numCPUOffloadLevels (Integer)
This is the number of candidate offload levels that the CellApp informs the CellAppMgr about. During load balancing, the CellAppMgr uses this information when considering where to move a cell boundary. The first level is calculated to offload maxCPUOffload. Addition levels get smaller expontentially. Each attempts to offload half what the previous level does.
The configuration options for load balancing based on the number
of entities are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under section <balance>/<demo>, and are
described below:
-
enable (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether the number of entities should be used to calculate load, rather than CPU load.
In normal situations, the server uses the CPU load on the CellApps to load balance. But sometimes it is desirable to use the number of entities per CellApp instead.
This may be useful, for example, when running multiple CellApps on a single machine for testing.
See also option demo/numEntitiesPerCell.
-
numEntitiesPerCell (Float)
If option demo/enable is true, then this option is used for calculating a CellApp's load.
The load is calculated as numEntities / numEntitiesPerCell.
See also option demo/enable.
The BaseApp configuration options are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under the section <baseApp>, and are described
below:
-
archiveEmergencyThreshold (Float)
This represents the amount of the DBMgr send window as a percentage that can be used for archiving entities. Archiving will be temporarily skipped if this threshold is reached. Valid values are from 0.0 to 1.0.
-
archivePeriod (Float)
Period length in seconds where each entity is written to the database for the purpose of disaster recovery. Each Entity is guaranteed to have an archive less than 2 x archivePeriod old. Setting it to zero switches off archiving.
A large value increases performance, but reduces the effectiveness of eventual disaster recovery. The opposite is true for a small value.
If secondary databases are disabled, this configuration option controls how often the entity is written to the primary database. In this case, this configuration option has a dramatic impact on the performance of the primary database when there are a large number of BaseApps. It is recommended to start with large values (a few minutes), and perform database testing and tuning before reducing it.
If secondary databases are enabled, this configuration option controls how often the entity is written to the secondary database. In this case, this configuration option can be set to a relatively small value (less than a minute) since it only impacts the BaseApp machine and the load is independent of number of BaseApps - unless the secondary database directory is on a shared network drive. For more details on secondary databases, see Server Programming Guide's chapter Secondary Databases.
This option is also available for CellAppMgr, controlling space data archiving.
-
backupPeriod (Float)
Number of seconds between backups of each base entity to its backup BaseApp. This value is rounded to the nearest game tick.
As a first level of fault tolerance, base entities can be copied to a backup BaseApp (i.e., backup to RAM), while cell entities are copied to their base entity. For more details on BaseApp and CellApp fault tolerance, see the document Server Programming Guide's chapter Fault Tolerance.
The value for this option is very dependant on the game. A small value means frequent backups, and consequently less lost data in case a BaseApp fails. But backups cost bandwidth and CPU on the BaseApp.
In general this period can be much smaller than the one specified in option archivePeriod.
Setting this to 0 disables backups.
See also option backupPeriod on CellApp Configuration Options.
-
backUpUndefinedProperties (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether undefined properties should be backed up.
Properties of an entity are defined in the entity's definition file. However, it is possible to define additional properties for this entity in the base script of this entity. For example, an additional property can be defined by initialising it in the constructor of this entity class. These additional properties are referred to as undefined properties.
If this option is set to true, undefined properties will be backed up and an error will be emitted for each of the properties that cannot be pickled. If this option is set to false, undefined properties will not be backed up. Default value is true.
-
clientOverflowLimit (Integer)
If the send window for the channel to the client grows larger than this many packets, the client is disconnected.
Generally, it is better to rely on inactivityTimeout to detect an unresponsive client and so this option should be set to greater than inactivityTimeout * gameUpdateHertz.
See also option inactivityTimeout on BaseApp Configuration Options
-
createBaseElsewhereThreshold (Float)
Threshold of local BaseApp load below which calls to BigWorld.createBaseAnywhere cause the new base entity to be created locally.
-
externalInterface
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
externalLatencyMax
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
externalLatencyMin
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
externalLossRatio
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
externalPorts/port (Integer)
Port that may be used for the BaseApp's external socket — the BaseApp can have more than one externalPorts/port definition.
This option is useful when BaseApp is running behind a firewall and NAT port mappings need to be set up.
If the BaseApps are run behind a firewall, then each BaseApp expected to run on a single machine should have an externalPort definition.
If this option is not specified, or all specified externalPorts are taken then the BaseApp will bind to any available port on the external interface.
<baseApp> <externalPorts> <port> 40013 </port> <port> 40014 </port> <port> 40015 </port> </externalPorts> </baseApp> -
inactivityTimeout (Float)
Number of seconds that a proxy will proceed without communication from the client before it considers the connection to be dead.
See also option clientOverflowLimit on BaseApp Configuration Options
-
internalInterface
For details, see General Configuration Options.
This tag is deprecated, and its use is not recommended. For details, see the document Server Overview's section Server Components → BWMachined → BWMachined Interface Discovery.
-
internalLatencyMax
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
internalLatencyMin
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
internalLossRatio
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
loadSmoothingBias (Float)
Value to smooth the load changes on a component by when calculating new load.
The BigWorld server uses the load on a component to perform its load balancing. Unfiltered, the load can change too quickly to be useful. The option loadSmoothingBias is used to smooth out this value.
The filtered value is calculated at each game tick as follows:
newSmoothedLoad = (1 - loadSmoothingBias) * oldSmoothedLoad + loadSmoothingBias * load
This option is also available for CellApps and CellAppMgr.
-
pythonPort (Integer)
Port that the Python telnet session listener should listen on.
If set to zero, then a random port is chosen.
If the option is missing, then the port number will be set according to the formula:
40,000 + BaseApp ID
If the desired port is not available in any case, then a random one is used.
This option is also available for CellApps.
-
reservedTickFraction (Float)
Fraction of tick time that should be remaining on current tick so the next one is considered to be pending.
This value is expressed as fraction. For example, setting it to 0.2 means that the next tick will be considered pending when there is still 20% of the current tick's time remaining.
Increasing this parameter will make the server more conservative in its CPU usage.
This affects how aggressive the method BigWorld.fetchFromChunks will be about yielding processing to the next tick.
This affects the
BigWorld.isNextTickPending()Python method.Note: This should rarely be changed from the default value.
-
sendAuthToClient (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether BaseApps must send authentication messages to clients (clients always send authentication to the server).
Use this feature to avoid hacking of clients, and prevent users from spoofing server messages to other clients.
Without this authentication, someone can send fake messages to clients, pretending to be the server (they will need the IP address of the client, and the port that the server is using, which can only be determined from the target client's data stream).
This option's value defaults to false, in order to save bandwidth.
-
sendWindowCallbackThreshold (Float)
The fraction of an entity channel's send window that needs to be used before the onWindowOverflow callback is called on the associated Base entity.
-
shouldResolveMailBoxes (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether a mailbox should be resolved to a Base entity, when possible. If a mailbox refers to a Base entity on the local BaseApp, the entity is used instead of the mailbox.
Although it is more efficient to have this option set, it is generally better to have it disabled. Having this enabled can lead to hard to find errors as behaviour changes depending on whether an entity happens to be local or not.
-
verboseExternalInterface (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether to generate verbose log output related to external network traffic.
-
warnOnNoDef (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether to generate a warning when Base entity properties are set that do not have a description in the entity's def file.
-
watcherValues (String)
This is not an actual configuration option, but instead a sub-section inside the section <baseApp>, used to set arbitrary watcher values for the BaseApp at initialisation time.
This might be useful when there is a watcher value with no corresponding entry on file
<res>/server/bw.xml.For example, to set value of logger/cppThresholds/baseapp.cpp to 2:
<baseApp> <watcherValues> <debug> <baseapp.cpp> 2 </baseapp.cpp> ...Do not use this feature if there is a parameter that can be set directly. Like all configuration options, this one is only evaluated once. It means that if there is an entry for watcherValues in
<res>/server/production_defaults.xml<res>/server/bw.xml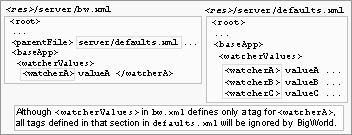
File hierarchy
The BaseApp secondary database configuration options are specified
in file <res>/server/
bw.xml under section
<baseApp>/<secondaryDB>, and are
described below:
-
enable (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether to use secondary databases.
For more details about secondary databases, see Server Programming Guide's section Secondary Databases.
-
maxCommitPeriod (Float)
Maximum number of seconds between each commit. Higher values will result in better performance. Lower values will reduce the amount of data loss in case of a total system crash.
Explicit
BigWorld.writeToDBcalls will always result in a commit. This option only affects the automatic archiving of entities.If set to zero or this option is empty, the value defaults to 5.
-
directory (String)
Directory where the secondary database files are stored. Secondary databases are SQLite files.
The secondary database files are cleaned up when the system shuts down. However, these files should not be treated as normal temporary files since they are crucial to the data recovery process in case of a complete system crash.
If the first character of the path is a / character, the path is treated as an absolute path. Otherwise, the path is treated as relative to the first
<res>path that contains the directory.
Note
It is not recommended to set the SQLite secondary database directory to reside on a network file-system. SQLite has specific requirements with regards to using file locking services from the file-system which may not be implemented properly for network file-systems.
It is recommended that each BaseApp machine has a dedicated space on a local file-system for storing secondary database files.
The BaseApp packet logging configuration options are specified in
file <res>/server/
bw.xml under section
<baseApp>/<packetLog>, and are described
below:
-
addr (String)
Client for which the packet's content should be logged.
The address is specified as dotted decimal format (e.g., 10.40.1.1).
If this option is empty, then all packets will be logged.
-
enable (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether to write all packets to a local log file proxy.log.
This can be useful for debugging.
-
flushMode (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether the log file should be flushed after each write.
This option is useful to ensure all log writes are captured if the BaseApp is crashing.
-
hexMode (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether the logged packets' contents should be written in hexadecimal.
The BaseApp ID configuration options are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under section <baseApp>/<ids>, and are
described below:
-
criticallyLowSize (Integer)
Minimum number of IDs in the BaseApp's available ID pool before the other limits are automatically adjusted.
The adjustment aims to help avoid this from occurring again.
-
desiredSize (Integer)
Target number of IDs in the BaseApp's available ID pool when requesting IDs to the parent broker ID (in case it fell below lowSize), or returning IDs to it (in case it rose above highLevel) — for CellApps and BaseApps, the parent ID broker is the CellAppMgr, while for CellAppMgr it is DBMgr.
-
highSize (Integer)
Maximum number of IDs in the BaseApp's available ID pool before IDs are returned to the parent ID broker — for CellApps and BaseApps, the parent ID broker is the CellAppMgr, while for CellAppMgr it is DBMgr.
ID recycling is currently disabled, so this value is actually never used.
-
lowSize (Integer)
Minimum number of IDs that should be available in the BaseApp's available ID pool before a request is sent to the parent ID broker to restore it to the value specified in configuration option desiredSize — for CellApps and BaseApps, the parent ID broker is the CellAppMgr, while for CellAppMgr it is DBMgr.
The client upstream bandwidth can be limited so as to prevent denial-of-service attacks from malicious clients, or errant script code that cause messages from the client to be sent in high volume. This can lead to Mercury channels within the server to become heavily loaded.
To prevent this, limits can be specified on the count and size of incoming messages from clients to BaseApps. Once hard limits are reached on the count/size of incoming messages, messages are buffered and played back over time. Once the hard limits on buffering are reached, clients are disconnected.
The configuration parameters are specified in the file
<res>/server/bw.xml
-
warnMessagesPerSecond (Integer)
This is a warning limit for the number of received messages from a client that are dispatched, measured in number of messages per second. When messages are received above this limit, a warning is emitted. No further warnings for this client of this type are emitted until the incoming message frequency drops below this limit.
-
maxMessagesPerSecond (Integer)
This is a hard limit for the number of received messages from a client that are dispatched, measured in number of messages per second. When messages are received above this limit, those and subsequent messages are buffered for later playback until the buffer is empty. The message queue for all clients are checked every tick to replay any eligible messages.
-
warnBytesPerSecond (Integer)
This is a warning limit for the throughput (in bytes) of received messages that are dispatched, measured in bytes per second. When this limit is exceeded, a warning is emitted. No further warnings for this client of this type are emitted until the incoming message data throughput drops below this limit.
-
maxBytesPerSecond (Integer)
This is a hard limit for the size of data (in bytes) in received messages that are dispatched per second. When messages are received above this limit, those and subsequent messages are buffered for later playback until the buffer is empty. The message queue for all clients are checked every tick to replay any eligible messages.
-
warnMessagesBuffered (Integer)
This is a warning limit for the number of received messages that may be buffered from the client. When this limit is exceeded, a warning is emitted. No further warnings for this client of this type are emitted until the number of queued messages drops below this threshold as a result of queue playback.
-
maxMessagesBuffered (Integer)
This is a maximum limit for the number of received messages that may be buffered from the client. When this limit is exceeded, the client is disconnected and any messages that are buffered are discarded and not dispatched.
-
warnBytesBuffered (Integer)
This is a warning limit for the total number of bytes that may be buffered for a client. When this limit is exceeded, a warning is emitted. No further warnings for this client of this type are emitted until the total size of buffered messages drops below this threshold as a result of queue playback.
-
maxBytesBuffered (Integer)
This is a maximum limit for the total number of bytes that may be buffered for a client. When this limit is exceeded, the client is disconnected and any messages that are buffered are discarded and not dispatched.
Auxiliary data bandwidth can be limited to control total cluster bandwidth usage, as well as per-client bandwidth usage. See the document Server Programming Guide's chapter Sending Auxiliary Data to the Client Via Proxy for details of auxiliary data streaming.
The configuration parameters are specified in the file
<res>/server/bw.xml
-
bitsPerSecondTotal (Integer)
This is the maximum amount of bandwidth the auxiliary data streaming may use per BaseApp. It is calculated per-tick.
Setting this value to 0 indicates that there is no total bandwidth limitation, while setting it below 640 (if <gameUpdateHertz> is 10Hz) will cause auxiliary data to never stream, as each auxiliary data message carries a 7-byte overhead.
-
bitsPerSecondPerClient (Integer)
This is the maximum amount of bandwidth the auxiliary data streaming will allocate to each client. It is calculated per-tick.
Setting this value to 0 indicates that there is no per-client bandwidth limitation, while setting it below 640 (if <gameUpdateHertz> is 10Hz) will cause auxiliary data to never stream, as each auxiliary data message carries a 7-byte overhead.
-
rampUpRate (Integer)
This is the bandwidth (in bits per second) which is added to the bandwidth available for the auxiliary data stream to a client, every tick, until <backLogLimit> packets are outstanding on that link or <bitsPerSecondPerClient> is reached.
Once it appears the auxiliary data stream is using nearly all of the spare bandwidth to a client, the streaming rate continues to ramp up at a small fraction of this value.
-
backLogLimit (Integer)
This is the limit on the number of unacknowledged packets which may have been sent to the client before auxiliary data streaming to that client is throttled. This is used to determine the spare capacity of the connection between the BaseApp and an individual client which may be used for auxiliary data.
The BaseAppMgr configuration options are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under section baseAppMgr, and are described
below:
-
baseAppOverloadLevel (Float)
Minimum load level that all BaseApps should reach for the system to be considered in overload, and thus reject new logins.
Similar overload levels are specified for for any CellApp (by option <cellAppOverloadLevel> — for more details, see CellAppMgr Configuration Options), and for DBMgr (by option <overloadLevel> — for more details, see DBMgr Configuration Options).
-
baseAppTimeout (Float)
Number of seconds for a BaseApp to respond before it is considered dead.
-
createBaseRatio (Float)
This option specifies the desired proportion of available BaseApps to consider as destinations for creating new base entities.
BaseAppMgr will periodically partition the available BaseApps into groups and allocate to each group a destination BaseApp to use for new base entity creations when using
createBaseAnywhere(). The destination BaseApps are chosen as the least-loaded BaseApps.For example, assume we have a cluster of 20 BaseApps and createBaseRatio is 4. The 20 BaseApps are partitioned into groups of 4 (5 groups in total). The 5 least-loaded BaseApps are chosen and allocated to each of the 5 groups as the destination to create Base entities using
createBaseAnywhere().This partitioning is randomised, and the calculation is done periodically according to the option updateCreateBaseInfoPeriod.
See also the option updateCreateBaseInfoPeriod.
-
hardKillDeadBaseApps (Boolean)
Determines if a non-responsive BaseApp will be terminated with a SIGQUIT signal.
Non-responsive BaseApps must be terminated in order for its backup to take over its IP address and ID. BaseApp non-responsiveness is determined by its backup, so a BaseApp running without a backup will never be reported as being non-responsive.
When this option is set to false, no signal is sent to the non-responsive BaseApp.
Only use this option for debugging, e.g., to attach a debugger to the hung process.
-
internalInterface
For details, see General Configuration Options.
This tag is deprecated, and its use is not recommended. For details, see the document Server Overview's section Server Components → BWMachined → BWMachined Interface Discovery.
-
internalLatencyMax
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
internalLatencyMin
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
internalLossRatio
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
overloadLogins (Integer)
Maximum amount of logins that will be accepted during the overload tolerance period (see the overloadTolerancePeriod option) before rejecting any further logins.
-
overloadTolerancePeriod (Float)
Number of seconds that logins will be accepted during a situation where the BaseApps are overloaded (see the baseAppOverloadLevel option). After this period of time, any further logins will be rejected.
-
updateCreateBaseInfoPeriod (Float)
Time (in seconds) between updating all BaseApps with information to assist them in creating entities on other BaseApps when using
BigWorld.createBaseAnywhere().See also the option createBaseRatio.
The Bots configuration options are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under the section <bots>, and are described
below:
-
controllerData (String)
Default data that the bot's controller will be created with (when bots are created, they get a controller associated with them to control their movement).
This may have different meanings for different controller types. For example, some controller types may interpret this as a filename to load data from.
-
controllerType (String)
Type of the controller to be created with bot.
-
interface (String)
Network adapter interface to use for game communication. For example: eth0. If not specified, the process will bind to all interfaces and report one of them. This should be appropriate in most situations.
See the BaseApp's configuration option externalInterface for accepted formats.
-
password (String)
Password that the bots should use when logging in to the server.
-
port (Integer)
Port on the server machine in which bots process will log to (only used if the option <serverName> is specified).
Ignored if bots automatically locates the LoginApp.
-
pythonPort (Integer)
Port that the Python telnet session listener should listen to.
-
randomName (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether a random suffix should be added to each bots name, in order to make them unique.
You should only set this option to false if you plan to use only a single bot. If you plan to use more than one bot, then you will need them to have different names — otherwise only the first one will be able to log in.
See also option username.
-
serverName (String)
Name of the server machine that the bots process should log in to (i.e., the machine running LoginApp).
If this option is empty, then the bots process will attempt to find an appropriate LoginApp on the local network.
-
shouldLog (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether messages generated by the bots process should be sent to the central logger.
-
shouldUseScripts (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether the bots process should use Python scripting for received entities.
If set to false, then received entities are effectively ignored. Turning this option on has a significant performance penalty.
-
standinEntity (String)
Default entity script to be used when a specific Entity type does not have its corresponding game script.
-
loginMD5Digest (String)
MD5 digest string (in hex readable form) for server login.
-
userName (String)
Username that bots should use when logging in to the server.
When randomName is true, this is the prefix before the randomly generated part of the name.
See also option randomName.
The CellApp configuration options are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under the section <cellApp>, and are described
below:
-
absoluteMaxControllers (Integer)
Number of controllers that an entity must have before an exception is raised on attempts to create a new controller on it.
-
aoiUpdateSchemes (Section)
This section contains a list of the different schemes that can be used when calculating the update rate of entities in an Area of Interest. The update rate of entities depends on their distance from the viewing client. The greater their update delta, the less frequent an entity's position is sent to the viewing client.
Each scheme contains the following values:
-
name - The name of the scheme.
-
minDelta - The update delta when the distance to the entity is 0 metres.
-
maxDelta - The update delta when the distance to the entity is maxAoIRadius metres.
The delta value for distances between this is calculated by a linear interpolation between these two points.
Setting minDelta to 1 and maxDelta to 101 means the delta for a given distance would be:
delta = 1 + 0.2 * distance
This means that entities at 20 metres (with a delta of 5) would be updated roughly 4.2 times more frequently than entities at 100 metres (with a delta of 21).
The scheme can be set for an entity with the
Entity.aoiUpdateSchemeproperty or for an entity pair with theEntity.setAoIUpdateScheme()method.<cellApp> ... <aoiUpdateSchemes> <scheme> <name> default </name> <minDelta> 1 </minDelta> <maxDelta> 101 </maxDelta> </scheme> <!-- Update rate is not dependant on distance. This could be used on entities that are in sniper scope, for example. --> <scheme> <name> sniper </name> <minDelta> 10 </minDelta> <maxDelta> 10 </maxDelta> </scheme> <!-- Update twice as frequently as other entities at the same distance. Useful for large entities like dragons. --> <scheme> <name> largeEntity </name> <minDelta> 0.5 </minDelta> <maxDelta> 50.5 </maxDelta> </scheme> </aoiUpdateSchemes> </cellApp> -
-
backupPeriod (Float)
Number of seconds between backups of each cell entity to its base entity. This value is rounded to the nearest game tick.
As a first level of fault tolerance, cell entities are copied to their base entities, while base entities can be copied to their backup BaseApps. For more details on BaseApp and CellApp fault tolerance, see the document Server Programming Guide's chapter Fault Tolerance.
The value for this option is very dependant on the game. A small value means frequent backups, and consequently less lost data in case a CellApp fails. But backups cost bandwidth and CPU on the CellApp.
Setting this to 0 disables backups.
See also options archivePeriod and backupPeriod on BaseApp Configuration Options.
-
checkOffloadsPeriod (Float)
Number of seconds between offload checks.
This is a periodic check if entities need to be offloaded, or new ghosts created.
-
chunkLoadingPeriod (Float)
Number of seconds between checks on the progress of loading and unloading chunks.
Chunk loading occurs in a separate thread, but this check in the main thread queues up more chunks for the loading thread to load (or unload).
-
defaultAoIRadius (Float)
The default AoI radius of new cell entities for proxy entities when they are created. See also the CellApp Python API's entry Main → Cell → BigWorld → Classes → Entity → setAoIRadius.
Note: This must not be larger than the option maxAoIRadius.
-
enforceGhostDecorators (Boolean)
Specifies whether to enforce the requirement of adding a decorator to methods that can safely be called on ghost entities.
When enabled, methods that have not been labelled as safe and are called on an entity that could be a ghost will generate a Python exception. To be considered safe, the method must either be described in the
.deffile or be decorated with@bwdecorators.callableOnGhost.import bwdecorators class Table( BigWorld.Entity ): @bwdecorators.callableOnGhost def getArea( self ): return self.width * self.height
-
entitySpamSize (Integer)
Number of bytes that an entity in a player's AoI can add to an update packet to that player before a warning message is displayed.
This can be useful to identify entities that are causing a lot of downstream network traffic.
-
expectedMaxControllers (Integer)
Minimum number of controllers an entity must have before a warning is generated on attempts to create a new controller on it.
-
fastShutdown (Boolean)
Specifies whether to avoid normal chunk unloading when the system is being shut down. This considerably speeds up the shutdown process.
-
ghostDistance (Float)
The distance in metres outside the active cell boundaries where entities will be ghosted.
-
ghostUpdateHertz (Integer)
Number of times per second channels to neighbouring CellApps are flushed.
Channels are created between neighbouring CellApps. Messages (such as ghost data) sent over these channels are not sent immediately, but are instead flushed periodically. This is done to avoid the high overhead of sending a packet.
If the value of this option is decreased, then there will be more lag for cross-cell communications.
Note: Bases always flush messages immediately.
-
internalInterface
For details, see General Configuration Options.
This tag is deprecated, and its use is not recommended. For details, see the document Server Overview's section Server Components, BWMachined, BWMachined Interface Discovery.
-
internalLatencyMax
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
internalLatencyMin
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
internalLossRatio
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
loadDominantTextureMaps (Boolean)
Specifies whether to load the terrain's dominant texture maps. By default, this flag is set to false.
Loading the dominant texture maps enables using features such as material kinds returned by BigWorld.collide.
-
loadSmoothingBias (Float)
Value to smooth the load changes on a component by when calculating new load.
The BigWorld server uses the load on a component to perform its load balancing. Unfiltered, the load can change too quickly to be useful. The option loadSmoothingBias is used to smooth out this value.
The filtered value is calculated at each game tick as follows:
newSmoothedLoad = (1 - loadSmoothingBias) * oldSmoothedLoad + loadSmoothingBias * load
This option is also available for CellAppMgr and BaseApps.
-
maxAoIRadius (Float)
Maximum AoI Radius for any entity. This will usually have the same value as the option ghostDistance.
See also defaultAoIRadius.
Note: Increasing this reduces the precision of the entity position data sent to the client. For example, doubling this will reduce the precision of the data by half, whereas halving it will double the precision. maxAoIRadius must not be larger than the option ghostDistance.
-
maxGhostsToDelete (Integer)
Maximum number of ghosts to be deleted from other cells on every offload check (the frequency of this check is set via checkOffloadsPeriod).
This option is useful for adding antihysteresis and for smoothing the load caused by ghost deletion.
-
minGhostLifespan (Float)
Minimum number of seconds for which a real entity will keep a ghost one.
This is useful for adding antihysteresis to the ghost creation and to the deletion process.
-
maxPhysicsNetworkJitter (Float)
Maximum number of seconds to allow for when network jitter when considering movement cheating.
The movement of a player may vary slightly due to variations in network latency. This value sets the level of tolerance for this jitter.
-
maxTickStagger (Float)
Maximum fraction of a tick that CellApp ticks will be staggered. This helps to avoid large spikes in network traffic. These large spikes can cause dropped packets with some network hardware.
The dropped packets are most likely to occur at your connection to the internet. If a large number of dropped packets are noticed, consider increasing this value.
This value should be between 0 and 1. 0 means that there is no staggering. 1 means that the CellApp ticks are staggered over the entire tick.
-
shouldNavigationDropPosition (Boolean)
This option determines whether calls to Entity navigation methods such as
Entity.navigateStep()should drop the Y position of the entity from the navigation mesh down onto the collision scene.This option is disabled by default.
-
navigationMaxClimb (Float)
Used in combination with shouldNavigationDropPosition to specify the maximum allowable distance an entity can be above the terrain before it is dropped. It is recommended this value match the largest maxClimb in the girths.xml
This option is 0.65 by default.
-
navigationMaxSlope (Float)
Used in combination with shouldNavigationDropPosition to specify the maximum slope of the navigation mesh in degrees. It is recommended this value match the steepest maxSlope in the girths.xml
This option is 45 by default.
-
navigatorUseGirthGrids (Boolean)
Specifies if the waypoint search optimisation scheme should be used.
Girth grid is an optimisation scheme for waypoint search in a chunk. When this scheme is used, a chunk is divided up into a set of 12x12 grids according to the girth provided (you can have a list of 12x12 grid set for different girth sizes). Every grid square contains a subset of waypoints that overlap the covered area in a chunk.
During a (waypoint) search, only targeted grid squares (i.e., subset of waypoints) are searched for the waypoint, instead of searching through the full set of waypoints. This scheme will generally improve the waypoint search performance.
-
obstacleTreeDepth (Integer)
Depth of the obstacle tree to create.
Higher numbers increase the speed of collision detection but use more memory.
-
pythonPort (Integer)
Port that the Python telnet session listener should listen on.
If set to zero, then a random port is chosen.
If the option is missing, then the port number will be set according to the formula:
50,000 + CellApp ID
If the desired port is not available in any case, then a random one is used.
This option is also available for BaseApps.
-
reservedTickFraction (Float)
Fraction of tick time that should be remaining on current tick so the next one is considered to be pending.
This value is expressed as fraction. For example, setting it to 0.2 means that the next tick will be considered pending when there is still 20% of the current tick's time remaining.
Increasing this parameter will make the server more conservative in its CPU usage.
This affects the
BigWorld.isNextTickPending()Python method.Note: This should rarely be changed from the default value.
-
sendWindowCallbackThreshold (Float)
The fraction of an entity channel's send window that needs to be used before the onWindowOverflow callback is called on the associated entity.
-
shouldResolveMailBoxes (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether a mailbox should be resolved to a Cell entity, when possible. If a mailbox refers to a Cell entity on the local CellApp, the entity is used instead of the mailbox.
Although it is more efficient to have this option set, it is generally better to have it disabled. Having this enabled can lead to hard to find errors as behaviour changes depending on whether an entity happens to be local or not.
-
treatAllOtherEntitiesAsGhosts (Boolean)
Puts the CellApp in a debugging mode in which a script running on it will see only its own entity as real — all other entities will be treated as ghosts.
Method calls, property access, and other functions will operate as if the other entities really are ghosts. This mean that:
-
Method calls will go via the network.
-
Property access will be read-only, and limited to CELL_PUBLIC (or more public) properties[1].
-
Many internal functions will not work, e.g., adding a new Controller.
This is very useful for testing how your scripts work when dealing with ghost entities, especially if two interacting entities are nearby and would consequently rarely be ghosts.
-
-
watcherValues (String)
This is not an actual configuration option, but instead a sub-section inside the section cellApp, used to set arbitrary watcher values for the CellApp at initialisation time.
This might be useful when there is a watcher value with no corresponding entry on
<res>/server/bw.xml.For example, to set the watcher value logger/cppThresholds/cellapp.cpp to 2:
<cellApp> <watcherValues> <debug> <cellapp.cpp> 2 </cellapp.cpp> ...Do not use this feature if there is a parameter that can be set directly.
Like all configuration options, this one is only evaluated once. It means that if there is an entry for watcherValues in
<res>/server/production_defaults.xml<res>/server/bw.xml also has an entry for watcherValues (even if different tags are specified in each one). This option is also available for BaseApps.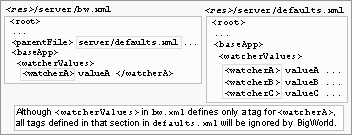
File hierarchy
The CellApp noise configuration options are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under section <cellApp>/<noise>, and are
described below:
-
horizontalSpeed (Float)
If an entity's horizontal speed exceeds this value (in metres per second), the entity makes a noise.
See Entity.makeNoise script method for more information. The event and info are 0 for noises generated this way.
-
standardRange (Float)
Distance in metres through which a noise is propagated.
This value is multiplied by the level of a noise. For details, see the CellApp Python API's entry Main → Cell → BigWorld → Classes → Entity → makeNoise.
-
verticalSpeed (Float)
If an entity's falling speed exceeds this value (in metres per second), the entity makes a noise.
This is done via script method Entity.makeNoise — for noises generated this way, the parameter event and info are set to 0. For details, see the CellApp Python API's entry Main → Cell → BigWorld → Classes → Entity → makeNoise.
The CellApp ID configuration options are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under section <cellApp>/<ids>, and are
described below:
-
criticallyLowSize (Integer)
Minimum number of IDs in the CellApp's available ID pool before the other limits are automatically adjusted.
The adjustment aims to help avoid this from occurring again.
-
desiredSize (Integer)
Target number of IDs in the CellApp's available ID pool when requesting IDs to the parent broker ID (in case it fell below lowSize), or returning IDs to it (in case it rose above highSize) — for CellApps and BaseApps, the parent ID broker is the CellAppMgr, and for CellAppMgr it is DBMgr.
-
highSize (Integer)
Maximum number of IDs in the CellApp's available ID pool before IDs are returned to the parent ID broker — for CellApps and BaseApps, the parent ID broker is the CellAppMgr, and for CellAppMgr it is DBMgr.
ID recycling is currently disabled, so this value is actually never used.
-
lowSize (Integer)
Minimum number of IDs that should be available in the CellApp's available ID pool before a request is sent to the parent ID broker to restore it to the value specified in configuration option desiredSize — for CellApps and BaseApps, the parent ID broker is the CellAppMgr, and for CellAppMgr it is DBMgr.
The CellApp profiles configuration options are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under section <cellApp>/<profiles>. It
contains sub-sections for enabling profiling of specific CellApp
functionality. All the profiling options specified below can be modified
after server startup on a per CellApp basis by using Watchers. The
values are exposed in the CellApp watcher tree under
profilesConfigs/<option>.
The list below details the available profiling sub-sections and options:
-
initGhost
The initGhost sub-options define profiling information relating to the initialisation of ghost entities. Specifically the maximum time taken and network stream size required to initialise ghost entities from their reals after which a WARNING message will be generated. The initialisation primarily consists of the streaming of ghosted entity properties.
-
sizeWarningLevel (Integer)
The size (in bytes) that an
initGhost() method receives before a WARNING message is displayed. -
timeWarningLevel (Float)
The amount of time (in seconds) that an
initGhost() method can take before a WARNING message is displayed. An example of the type of message generated is as follows.WARNING Profile initGhost/timeWarningLevel exceeded (Creature 23 of size 12338 bytes took 0.00477 seconds)
-
-
initReal
Similar to the initGhost option, the initReal sub-options define profiling information relating to the initialisation of real entities. Specifically the maximum time taken and network stream size required to initialise real entities from their reals after which a WARNING message will be generated. The initialisation primarily consists of the streaming of entity properties.
-
sizeWarningLevel (Integer)
The size (in bytes) that an
initReal() method receives before a WARNING message is displayed. An example of the type of message generated is as follows.WARNING Profile initReal/sizeWarningLevel exceeded (Creature 13 of size 68765 bytes took 0.3726 seconds)
-
timeWarningLevel (Float)
The amount of time (in seconds) that an
initReal() method can take before a WARNING message is displayed.
-
-
onLoad
The
onLoad() operation is invoked when creating a real entity that had been offloaded from another CellApp.-
sizeWarningLevel (Integer)
The size (in bytes) that an
onLoad() method receives before a WARNING message is displayed. An example of the type of message generated is as follows. The size is considered as the total size of the real entity and which is comprised of non-ghosted (i.e. CELL_PRIVATE) properties and other state information such as entities in the AoI, controller state etc. -
timeWarningLevel (Float)
The amount of time (in seconds) that an
onLoad() method can take before a WARNING message is displayed.
-
-
backup/sizeWarningLevel (Integer)
backup is the operation of performing a fixed point in time copy of the cell entity to the database (via the base). The size (in bytes) is the maximum persistent size of the entity (i.e. only persistent properties) after which a WARNING message is displayed.
The CellAppMgr configuration options are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under the section <CellAppMgr>, and are described
below:
-
archivePeriod (Float)
Number of seconds between database writes of space data and game time, for the purpose of disaster recovery.
The default setting of zero switches off database writes of space data completely, and disables periodic database writes of game time.
If your space data must persist across server restarts, or your game time needs to be monotonic across server restarts, you should change this value.
A large value increases performance, but reduces the effectiveness of eventual disaster recovery. The opposite is true for a small value.
Please note that unlike the BaseApp configuration option of the same name, this configuration option is not affected by the use of secondary databases. The data is always written to the primary database. It is recommended to start with large values (a few minutes), and perform database testing and tuning before reducing it.
This option is also available for BaseApps, controlling entity archiving.
-
cellAppLoad/lowerBound (Float)
Minimum average load that a CellApp must achieve before being retired.
This value is a fraction, and its range is 0.0 through 1.0.
Retiring cells is mainly useful if low loads are causing instability in load balancing and causing excessive chunk loading. This value can typically be kept very small (or zero).
This value must be less than the cellAppLoad/upperBound.
See also option cellAppLoad/upperBound.
-
cellAppLoad/safetyBound (Float)
Limit that the load balancing can increase a cell's load to.
This value has to be greater than cellAppLoad/upperBound.
In some situations, such as adding a new cell, some cells may have their load temporarily increased.
-
cellAppLoad/safetyRatio (Float)
Cell's average load safety ratio.
When the average load of the cells in a space is high, the limit that the load balancing can safely increase a cell's load to is calculated by multiplying this value by the average load. The real boundary is calculated as:
max( cellAppLoadSafetyBound, avgCellAppLoad * cellAppLoadSafetyRatio )
-
cellAppLoad/upperBound (Float)
Minimum average load that a CellApp must achieve before a new cell is considered to be required.
This value is a fraction, and its range is 0.0 through 1.0.
It is generally desired to keep this value small to make use of most CellApps all of the time. Doing so, allows for faster response to increases in load.
This value must be greater than the cellAppLoad/lowerBound.
See also option cellAppLoad/lowerBound.
-
cellAppLoad/warningLevel (Float)
Minimum value that average load of CellApps must achieve (when there are no other CellApps available to share the load) before warning messages are sent to the log.
-
cellAppLoad/overloadLevel (Float)
Minimum load level that any CellApp should reach for the system to be considered in overload, and thus reject new logins.
Similar overload levels are specified for all BaseApps (by option <baseAppOverloadLevel> — for details, see BaseAppMgr Configuration Options), and for DBMgr (by option <overloadLevel> — for details, see DBMgr Configuration Options).
-
cellAppTimeout (Float)
Number of seconds for a CellApp to respond before it is considered dead.
-
hardKillDeadCellApps (Boolean)
Determines if a non-responsive CellApp will be terminated with a SIGQUIT signal.
CellApp non-responsiveness is determined by cellAppTimeout option.
It is important to terminate the non-responsive CellApp, in order to prevent duplicate entities, since some of the entities on the non-responsive CellApp will be recreated on neighbouring CellApps[2].
When this option is set to false, no signal will be sent to the non-responsive CellApp. This option should only be used for debugging purposes, e.g., to attach a debugger to the hung process.
-
internalInterface
For details, see General Configuration Options.
This tag is deprecated, and its use is not recommended. For details, see the document Server Overview's section Server Components, BWMachined, BWMachined Interface Discovery.
-
internalLatencyMax
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
internalLatencyMin
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
internalLossRatio
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
loadBalancePeriod (Float)
Number of seconds between adjustments of the cell boundaries to improve the load balance on CellApps.
-
loadSmoothingBias (Float)
Value to smooth the load changes on a component by when calculating new load.
The BigWorld server uses the load on a component to perform its load balancing. Unfiltered, the load can change too quickly to be useful. The option loadSmoothingBias is used to smooth out this value.
The filtered value is calculated at each game tick as follows:
newSmoothedLoad = (1 - loadSmoothingBias) * oldSmoothedLoad + loadSmoothingBias * load
The CellAppMgr further smooths the CellApp loads when it is informed of them.
This option is also available for BaseApps and CellApps.
-
maxLoadingCells (Integer)
Maximum number of cells that the meta-load balancing will try to add to a space to help it initially load its geometry.
To disable this feature, set this value to 0.
See also minLoadingArea.
-
metaLoadBalanceScheme (Integer)
The type of scheme that should be used to determine which Spaces should be a priority to meta load balanced. Current valid values are:
-
0 - Largest Space First
The largest space contained in the most loaded group of connected CellApps will be chosen as the candidate for adding a new Cell into.
-
1 - Smallest Space First
The smallest space contained in the most loaded group of connected CellApps will be chosen as the candidate for adding a new Cell into. This will enable the space to migrate off onto another CellApp thus reducing the overall load of the heavily loaded group.
-
-
metaLoadBalancePeriod (Float)
Number of seconds between checking whether any cells should be added to or removed from any spaces to improve the load balance on CellApps.
-
minLoadingArea (Integer)
Minimum average area (in square metres) that the cells in a space must have for it to be added by the meta-load balancing when attempting to initially load the geometry of a space.
If the average area is less than this value, then no more cells will be added to the meta-load balancing — this is meant to prevent too many cells being allocated to small spaces.
The number of cells that will be used for loading a space can be thought of as:
See also maxLoadingCells.
-
overloadTolerancePeriod (Float)
Number of seconds that logins will be accepted during a situation where the CellApps are overloaded (see the cellAppOverloadLevel option). After this period of time, any further logins will be rejected.
-
shouldLimitBalanceToChunks (Boolean)
Determines if the loaded chunks of cells should be considered when load balancing.
This is enabled by default, so that load balancing will not cause a cell to cover an area that has not yet been loaded.
The DBMgr configuration options are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under the section <dbMgr>, and are described
below:
-
allowEmptyDigest (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether DBMgr should allow clients to log in with an empty MD5 digest.
When a client logs in, an MD5 digest of the entity definitions is sent to the server. This is to ensure that the client is using resources consistent with the server's.
This should be true if you are using either the simple Python example client, as found in
bigworld/src/examples/client_integration/python/simple, or bots to log in, since those programs do not read the entity definition files (named<res>/scripts/entity_defs/<entity>.def). -
databaseName (String)
Only valid when the MySQL database layer is used.
Name of the underlying database to use.
-
dumpEntityDescription (Integer)
Level of logging information generated when loading entity definition files (named
<res>/scripts/entity_defs/<entity>.def).The possible values are described in the list below:
-
0 — No log is generated.
-
1 — Brief details about the entity are generated.
-
2 — Full listing of entity is generated.
-
> 2 — Full listing of entity is generated with details of database persistence.
-
-
host (String)
Only valid when the MySQL database layer is used.
Machine where the database is running.
The localhost identified can be used to refer to the current machine.
-
internalInterface (String)
For details, see General Configuration Options.
This tag is deprecated, and its use is not recommended. For details, see the document Server Overview's section Server Components, BWMachined, BWMachined Interface Discovery.
-
internalLatencyMax (Float)
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
internalLatencyMin (Float)
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
internalLossRatio (Float)
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
numConnections (Integer)
Only valid when the MySQL database layer is used.
Number of connections to make to the underlying database.
This must be greater than or equal to 1. The default is 5.
-
overloadLevel (Float)
Minimum load level that DBMgr should reach for the system to be considered in overload, and thus reject new logins.
Similar overload levels are specified for all BaseApp's (using baseAppOverloadLevel — for details, see BaseAppMgr Configuration Options), and for any CellApp (using cellAppOverloadLevel — for details, see CellAppMgr Configuration Options.
-
overloadTolerancePeriod (Float)
Number of seconds that logins will be accepted during a situation where the CellApps are overloaded (see the overloadLevel option). After this period of time, any further logins will be rejected.
-
password (String)
Only valid when the MySQL database layer is used.
Password to be used when the DBMgr connects to the underlying database.
-
port (String)
Only valid when the MySQL database layer is used.
Port to be used when the DBMgr connects to the underlying database. Set it to 0 to use the MySQL default port.
-
syncTablesToDefs (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether changes to entity definition should be replicated to the MYSQL database.
The possible values are described below:
-
false
No changes will be made to MySQL database structure.
-
true
Make all necessary changes to the database structure to match the entity definitions. This includes deleting redundant columns and tables.
DBMgr will fail to start if the database structure does not exactly match the entity definitions.
This option is convenient during development as entity definitions change frequently. During production it is recommended to set this option to a safe mode (i.e., false), then manually update the MySQL database structure by running the sync_db tool.
-
-
type (String)
Type of database to use. Current options are: xml and mysql.
-
unicodeString/characterSet (String)
This is the character set that the database should use to store UNICODE_STRING properties in the database. This is set to utf8 by default. It should be rare that this should ever be changed. For more details on the effects of setting this option please refer to the Server Programming Guide, chapter Character Sets and Encodings, section UNICODE_STRING storage.
See the option dbMgr/unicodeString/collation for for information on setting the collation type.
-
unicodeString/collation (String)
This is the default collation that the database associates with UNICODE_STRING properties. This is set to utf8_bin by default. This can be set to utf8_general_ci, for example, if case insensitive lookups on identifier fields are required. With this setting, identifiers need to be unique using a case-insensitive comparison. For more details on the effects of setting this option please refer to the Server Programming Guide, chapter Character Sets and Encodings, section Sorting search results.
See dbMgr/unicodeString/characterSet for setting the character set.
-
username (String)
Only valid when the MySQL database layer is used.
Username used when the DBMgr connects to the underlying database.
The options for data consolidation tool are located in the
<dbMgr>/<consolidation> section of the server
configuration file <res>/server/bw.xml
For more detail about the data consolidation process, see Data Consolidation Tool).
-
directory (String)
Directory where the data consolidation tool puts temporary secondary database files copied from BaseApp machines. These files are automatically deleted when the data consolidation process completes.
If the first character of the path is a / character, the path is treated as an absolute path. Otherwise, the path is treated as relative to the first
<res>path that contains the directory.
Note
It is not recommended to set the SQLite secondary database directory to reside on a network file-system. SQLite has specific requirements with regards to using file locking services from the file-system which may not be implemented properly for network file-systems.
It is recommended that each BaseApp machine has a dedicated space on a local file-system for storing secondary database files.
The options specific to using XML as the database type are located
in the <dbMgr>/<xml> section of the server
configuration file <res>/server/bw.xml
Note
The XML database is written in the main thread. If saving takes a long time, this can block any processing by DBMgr. To avoid this, disable archiving and automatic saving.
-
archivePeriod (Float)
Number of seconds between making an archive of the XML database. The newest archive is
scripts/db.xml.1thenscripts/db.xml.2etc.To disable archiving, set this value to 0.0.
-
numArchives (Integer)
Number of archives to keep of the XML database.
-
savePeriod (Float)
Number of seconds between saving the XML database to disk. The previous file is
backed up as scripts/db.xml.bak.To disable backing up, set this value to 0.0.
The LoginApp configuration options are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under the section <loginApp>, and are described
below:
-
allowLogin (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether login attempts should be accepted.
This is useful when the server needs to be started without accepting logins for a while (e.g., to have the server load chunks before allowing logins).
Logins can be enabled by setting allowLogin watcher on each LoginApp to true — for a simpler way to achieve this for all running LoginApps, see control_cluster.py's set command[3].
-
allowProbe (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether login probes should be accepted.
It is recommended to have this flag set to false for servers running on the public Internet.
This setting can be changed at runtime by settings the allowProbe watcher.
See also option logProbes.
-
allowUnencryptedLogins (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether a client sending a plaintext login request and/or a null session key should be allowed to connect.
This flag should only be used for testing purposes. Setting this flag to true on a production system is not recommended.
-
externalInterface
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
externalLatencyMax
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
externalLatencyMin
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
externalLossRatio
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
internalInterface
For details, see General Configuration Options.
This tag is deprecated, and its use is not recommended. For details, see the document Server Overview's section Server Components, BWMachined, BWMachined Interface Discovery.
-
internalLatencyMax
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
internalLatencyMin
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
internalLossRatio
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
loginRateLimit (Integer)
Specifies the number of allowed logins when rate-limiting. As many logins as this are allowed during each rate-limiting period as specified in option rateLimitDuration.
For example, if option loginRateLimit is set to 100, and option rateLimitDuration is set to 10, then 100 logins will be allowed every 10 seconds. If the login rate limit quota is exceeded during this period, no further logins are allowed until the start of the next 10 second period.
See also option rateLimitDuration.
-
logProbes (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether login probe attempts should generate a log message.
This might be useful for servers running on the public Internet, to verify users who are attempting to probe and/or hack the server.
See also option allowProbe.
-
externalPorts/port (Integer)
Port that the LoginApp should listen to for login requests.
If set to zero, then a random port is chosen, which is useful when running multiple BigWorld server instances in a LAN. The client would then need to auto-detect the available servers. For more details, see Auto-Detection of LoginApps.
Multiple port entries may be specified if necessary in order to provide a range of ports to use on a machine. This is useful if multiple LoginApps are intended to be used on the same machine, and would generally be used in conjunction with the option shouldShutDownIfPortUsed. For example:
<loginApp> <externalPorts> <port> 20013 </port> <port> 20014 </port> <port> 20015 </port> </externalPorts> <shouldShutDownIfPortUsed> true </shouldShutDownIfPortUsed> </loginApp> -
maxLoginDelay (Float)
If the response from the LoginApp to the client is lost, the successful login needs to be resent to the client. This setting is the number of seconds that a successful login attempt is kept.
-
privateKey (String)
This is the filename to read the LoginApp's RSA private key from. This is the key that is used to decrypt the client's login credentials.
Please see Encrypting Client-Server Traffic for more information about the encryption support in BigWorld.
-
rateLimitDuration (Integer)
Specifies the rate-limiting time period in seconds. As many logins as is specified in option loginRateLimit are allowed during every one of these periods.
For example, if option loginRateLimit is set to 100, and option rateLimitDuration is set to 10, then 100 logins will be allowed every 10 seconds. If the login rate limit quota is exceeded during this period, no further logins are allowed until the start of the next 10 second period.
Setting this value to 0 disables login rate limiting.
See also option loginRateLimit.
-
registerExternalInterface (Boolean)
If set to true, the LoginApp's external interface will be registered with bwmachined. This may be useful during development to allow clients to discover running server. This should be set to false in a production environment.
-
shouldShutDownIfPortUsed (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether the LoginApp should shut down if the specified port to listen to is not available.
If set to true, the LoginApp will shut down if the specified ports to listen to is not available. If set to false, the LoginApp will find another port to listen to.
See also option port.
-
shutDownSystemOnExit (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether the server should be also shut down when LoginApp is shut down.
If set to true, then a controlled shutdown is performed on the server.
-
verboseExternalInterface (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether to generate verbose log output related to external network traffic.
The Reviver configuration options are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under the reviver section, and are described below:
-
internalLatencyMax
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
internalLatencyMin
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
internalLossRatio
For details, see General Configuration Options.
-
pingPeriod (Float)
Number of seconds between pings sent to monitored processes for execution check purposes.
Reviver's monitor processes periodically by pinging them to check that they are still running and functioning normally.
See also option subjectTimeout.
-
reattachPeriod (Float)
Number of seconds between each time that Reviver checks processes to determine if it can monitor them.
If another Reviver stops monitoring a process, this option allows this Reviver to start monitoring that process.
See also option subjectTimeout.
-
shutDownOnRevive (Boolean)
Flag indicating whether the Reviver itself should be shut down after reviving a monitored process.
This is usually set to true, since once a Reviver has started a process, that machine should probably be considered busy.
See also option subjectTimeout.
-
subjectTimeout (Float)
Number of seconds that a monitored process will wait for a response from its current Reviver before accepting to be monitored by another one.
If a monitored process does not receive a response from its current Reviver, then it is assumed that the Reviver has been stopped after reviving another one of its monitored processes (this behaviour is set by option shutDownOnRevive).
See also options pingPeriod, reattachPeriod and shutDownOnRevive.
-
timeout (Float)
Number of seconds that can be missed by a monitored process before Reviver assumes it is dead.
The BaseAppMgr configuration options are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under section <reviver>/<baseAppMgr>.
These are the same as general Reviver options, but specific to
BaseAppMgr. If the setting is not specified, then the general one is
used. For details on these options, see Reviver Configuration Options.
The options are listed below:
-
pingPeriod (Float)
-
subjectTimeout (Float)
-
timeoutInPings (Integer)
The CellAppMgr configuration options are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under section <reviver>/<cellAppMgr>.
These are the same as general Reviver options, but specific to
CellAppMgr. If the setting is not specified, then the general one is
used. For details on these options, see Reviver Configuration Options.
The options are listed below:
-
pingPeriod (Float)
-
subjectTimeout (Float)
-
timeoutInPings (Integer)
The DBMgr configuration options are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under section <reviver>/<dbMgr>. These
are the same as general Reviver options, but specific to DBMgr. If the
setting is not specified, then the general one is used. For details on
these options, see Reviver Configuration Options.
The options are listed below:
-
pingPeriod (Float)
-
subjectTimeout (Float)
-
timeoutInPings (Integer)
The LoginApp configuration options are specified in file
<res>/server/bw.xml
under section <reviver>/<loginApp>. These
are the same as general Reviver options, but specific to LoginApp. If
the setting is not specified, then the general one is used. For details
on these options, see Reviver Configuration Options.
The options are listed below:
-
pingPeriod (Float)
-
subjectTimeout (Float)
-
timeoutInPings (Integer)
[1] For more details, see the Server Programming Guide's section Properties → Data Distribution.
[2] For details, see CellApp Fault Tolerance.
[3] For details on control_cluster.py, see Control Cluster.
